Treating minor cuts and grazes
It is possible to control minor cuts and grazes by applying pressure on the cut. The injured body part should be raised above the heart. If you don’t have a sterile dressing, use a hand, tea towel or T-shirt. Whoever is treating the wound should wash their hands and wear gloves made of latex if possible.
Home care for minor cuts
Stop bleeding by placing pressure on the area with a gauze pad or clean cloth. Then rinse the cut thoroughly with cool water after bleeding stops. Please use a soft washcloth and soap to clean the wound. Iodine peroxide and hydrogen peroxide will damage living cells and should not be used directly on wounds. To remove glass gravel or other foreign matter use tweezers cleaned with rubbing alcohol. Some of the wounds such as scrapes covering a large area should be kept moist to help reduce scarring. It’s best to use sealed bands for this purpose.
Before you try to stop the bleeding
Make use of medical gloves if available before applying direct pressure. If gloves are not available, use cloth, plastic bags, or the cleanest material. Have the injured person hold direct pressure on the wound if possible and elevate the injured area.
Apply pressure
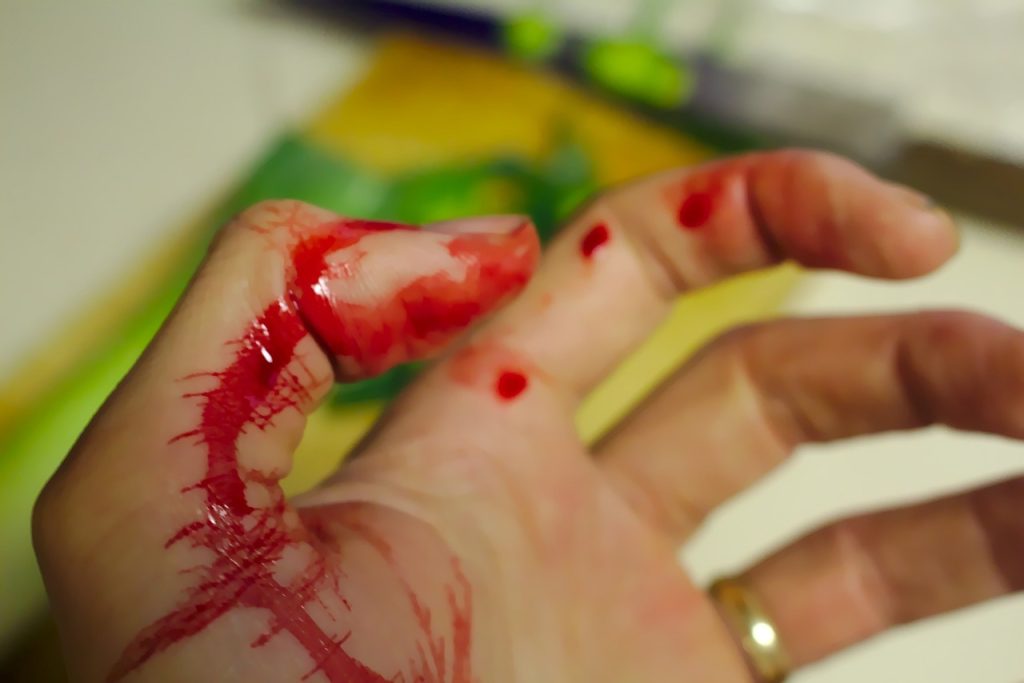
Applying pressure to the wound is the best way to stop it from bleeding. Place clean and dry material such as a bandage towel or cloth on wounds. Maintain constant pressure until bleeding stops.
Stop the bleeding
Have the injured person lie down and raise the bleeding site. Remove any visible objects that are easy to remove in the wound. For 15 minutes, apply steady pressure. Mild bleeding usually stops on its own or slows down to an ooze. If the bleeding causes blood to accumulate in the wound site, the risk of infection increases.
Raise the affected area
It will also help stop the bleeding of the blood. If the injury is to the hand or arm, raise it above the head. If it is to a lower limb, lie down and raise the affected area above the heart.
Ice

Applying ice to a wound will constrict the blood vessels allowing a clot to form more quickly and stop bleeding. You can wrap the ice in a clean dry cloth and place it on the wound.
Petroleum jelly

Many cosmetics contain petroleum jelly. This product contains a mixture of oils and waxes which can be used to protect the skin. As a homemade remedy, it can also help stop bleeding.
Antiperspirant
Antiperspirants can constrict blood vessels to help clot a wound. The use of aluminum chloride in a 2015 study was shown to be a fast and effective way to control minor external bleeding.
Mouthwash
The alcohol in mouthwash acts as an astringent and applying it to a wound helps the blood to clot more easily. Bleeding in the mouth can be treated with a substance called amicar.
How to stop a nosebleed
The following steps can be used to stop a nosebleed. Place your body upright and lean slightly forward. You can breathe through your mouth. Try to catch the blood with a tissue or a damp washcloth. Don’t bend over, strain or lift anything heavy after the bleeding stops. Blow or rub your nose for a while.
Preventing infection
When bleeding stops, it’s important to keep the wound clean. Rinse the wound with cold water and use soap to wash the surrounding area. If possible, remove dirt or debris from inside the wound with a tweezer.
When to see a doctor
Bleeding is the number one preventable cause of death in trauma. Most minor bleeding can be stopped at home using simple home remedies. Minor wounds should be covered with a bandage to prevent infection once the bleeding has stopped.
When should I go to the emergency room if I have a nosebleed?
If you can’t stop the bleeding after a few minutes of applying direct pressure on your nose, you should call your healthcare provider. You vomited because you were having difficulty breathing, the bleeding is rapid or the blood loss is large. Your nosebleed follows a blow to the head or a serious injury.
Can you die from a nosebleed?
Four out of every million deaths in the United States are caused by nosebleeds. Nosebleeds that occur higher on your septum or deeper in your nose may be harder to control than others.
What is epistaxis?
A nosebleed is a loss of blood from the tissue inside your nose. It only affects one nostril. Most nosebleeds are not serious.
Who gets epistaxis?
Anyone can get a disease. Most people will have at least one case during their lifetime. Some people have a nosebleed more often than others. Children are more prone to nosebleeds because of dry air, colds, allergies and sticking fingers into their noses. In older adults, blood may take longer to clot.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.